Fermentation (English)
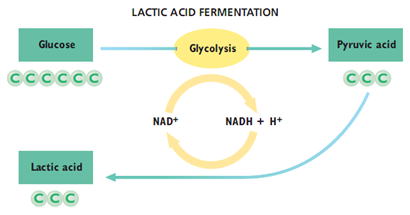
When oxygen is present, cellular respiration continues as pyruvic acid enters the pathways of aerobic respiration . In anaerobic conditions (when oxygen is absent), however, some cells can convert pyruvic acid into other compounds through additional biochemical pathways that occur in the cytosol. The combination of glycolysis and these additional pathways, which regenerate NAD, is known as fermentation. The additional fermentation pathways do not produce ATP. However, if there were not a cellular process that recycled NAD from NADH, glycolysis would quickly use up all the NAD in the cell. Glycolysis would then stop. ATP production through glycolysis would therefore also stop. The fermentation pathways thus allow for the continued production of ATP. There are many fermentation pathways, and they differ in terms of the enzymes that are used and the compounds that are made from pyruvic acid. Two common fermentation pathways result in the production of lactic acid and ethyl ...